Describe the Structure of a Phospholipid Bilayer
Explain how this is an adaptation to living in the intestines. D carbohydrates function as membrane channels.

Phospholipid Structure Function What Is A Phospholipid Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
C protein molecules that perform important cellular functions float in a lipid bilayer.

. Lamblia can attach itself with its sucker. Describe how the structure of a cholera bacterium is different. E nonpolar ends of phospholipids are exposed to water inside and outside the cell.
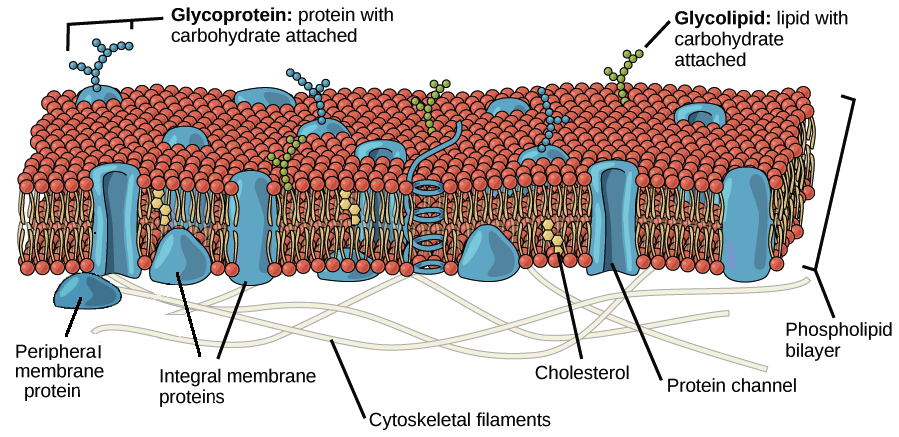
Molecules that dissolve in fat can pass through easily while molecules that dissolve in. It is caused by the microorganism Giardia lamblia. The eukaryotic plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded in it.
A Flagellum Sucker Nucleus Ribosomes Name one. How a Phospholipid Bilayer Is Both Hydrophobic and. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane Figure 316.
A Describe the structure of the. The structure of the lipid bilayer allows only small non-polar substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through the cell membrane down their concentration gradient by simple diffusion. For instance the plasma membrane of cells that in multicellular organisms specialize in absorption are often folded into fingerlike.
This figure depicts the lipid bilayer and the structure of a phospholipid. As discussed in the context of bacterial cell membranes the plasma membranes of eukaryotic cells may also adopt unique conformations. As membrane components phospholipids are selectively permeable also called semi-permeable meaning that only certain molecules can pass through them to enter or exit the cell.
The drawing shows some of the structures present in G. L mark Giardiasis is an intestinal disease. The female reproductive hormones estrogen and progesterone are synthesized by _____ subcellular structure.
Structure Of The Plasma Membrane Article Khan Academy


No comments for "Describe the Structure of a Phospholipid Bilayer"
Post a Comment